Have you ever had this happen to you? You've spent the afternoon getting all your sounds perfectly tweaked for tonight's gig, but when you get there and start playing, everything sounds really..... not right? Things sound overly bright, but also a little 'woofy', so you have to fix things on the fly as the night goes along and silently curse your amp. The next day, when you set things back up at home, you go back to re-tweak your sounds, and suddenly they sound okay again. Are you going nuts? Have your ears suddenly lost it? Is there a problem with your amp? Don't worry, they're both fine; you've just been bitten by the Fletcher-Munson curves.
"What's this?", you ask. "I thought Thurman Munson was a catcher for the Yankees, not a pitcher, (although he hit the curve pretty well) and who the heck is this Fletcher guy?" Well, aside from the fact that the baseball trivia part of your brain is functioning just fine, there's a whole other story going on here. Although it may look a little daunting (especially that graph you see looming below), it's really pretty simple, so just bear with us a moment for the inside poop.
Fletcher and Munson were researchers at Bell Laboratories who demonstrated, in 1933, that the human ear (and brain) perceive different frequencies in a shifting manner dependent on level. Their measurements showed that your ear is most sensitive to frequencies in the range of 3-4kHz, and that frequencies above and below those points must be louder, in absolute terms, in order to be perceived as being of equal loudness. They also showed that the amount of increase of loudness in those other frequencies to achieve that perceived equality varies depending on what the overall SPL (Sound Pressure Level), or sound intensity, is in the first place. These discoveries helped kick off a whole new area of study called 'psychoacoustics' and brought you, among other things, that little button on your stereo labeled 'Loudness'. When they mapped our these curves (also known as 'Equal Loudness Contours') they looked something like this:
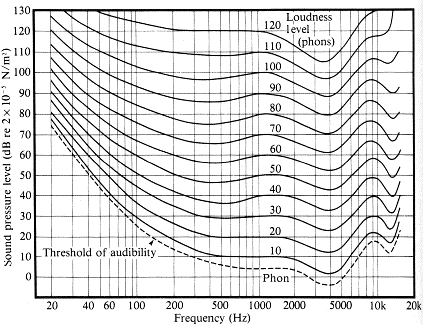
When you look at these curves, you'll notice that when the 3-4 kHz range is at 0dB (or just barely audible), frequencies at 20Hz (about as low as you can perceive a distinct tone) have to be raised over 60 dB (which is 64 times as loud. Remember that decibels are measured on a logarithmic scale, so this is also 1000 times the power) to be perceived as being the same volume. On the other hand, when the base level for our 'home' frequencies is raised to 80dB, the lowest frequencies only have to be raised 10dB (or be twice as loud) to be perceived as being the same volume.
Now what does this mean to you as a guitarist? Well, as we alluded to above, you'll notice that the curves flatten out substantially as you get louder. This means that the sounds you tweak up in your living room will have the low and high end boosted substantially (the infamous 'smile curve') to make those frequencies sound equally loud to the midrange frequencies to which you're most sensitive. When you take those sounds that you designed at around 60-70 dB (which is your basic living room, not gonna wake the neighbors or overly annoy the family level) and turn them up to the average 90dB+ stage levels, those same high and low frequencies will suddenly seem overly exaggerated making everything sound simultaneously painfully bright, yet woofy (kinda like a bad wine tasting description). Not only that, but those midrange frequencies (where the fundamental information about just which note you're playing live) are being overwhelmed by that, now excessive, high and low frequency information.
So what's a fella to do? Well, if you can manage it without driving everyone crazy, studies have determined that the optimum level for reference mixing (which would apply to sound design as well) is about 85dB. This is loud enough to start flattening out the curve, but not so loud as to seriously hurt yourself (unless you do it for 14 hours straight) Get yourself an inexpensive SPL meter, set it to 'A' weighting (which shoots for the equivalent of the human hearing sensitivity) crank up your amp so you're averaging 85dB, and tweak in your patches. Of course, 85dB is, to put it in easily understandable terms, 'pretty darn loud', so this isn't something you can do a 2 AM when you can't sleep 'cause you're worrying about sounding just right for the next gig. The next best thing is to schedule a rehearsal with the rest of your band where you can crank it up, and make your final tweaks while the rest of the guys are there cracking jokes about obsessive/compulsive guitarists. Your third option, and probably the easiest, is to study the curves above carefully, and remember that if your sound is a little mid-heavy and seems a little bit dull at living room level, it's probably going to be about right when you crank that sucker up live. Here's a potential approach. Next time you're tweaking up a tone or two, make two versions; one that sounds right at living room levels, and one that you think, using the stuff you've learned here, should sound about right at stage levels. When you play live, leave the first one alone, and tweak the second one (if necessary), then go back the next day and compare the two. Pay attention to how they differ from each other. Now try and make a couple more, using the same process. After you've done this a few times, you should be getting a pretty good feel for just what you'll have to do to get 'em right the first time. Presto, you're one step closer to that elusive Ph.D in Tone.
Now, if you're the type that really wants to dive in and get some serious information overload, you might want to try going here. This is one of the coolest online reference sites we've found in a long time, courtesy of Campanella Associates, an acoustic consulting firm. It's a fairly complete audio text and tutorial, that will give you more than you thought you needed to know (but not more than you should) about audio, acoustics, and sound.
